Wireless network is one of the types of computer network that is not entirely dependent on a wired medium to establish communications between the user and the network. A wired network has some shortcomings that wireless network addresses, such as mobility and dependence to be tethered to a wire or cable. A user can easily connect multiple mobile devices to the network seamlessly. Wireless communication travels through free space using radio waves without the limitation and protection of a wired medium like copper or fiber.
In free space, many variables should be taken into consideration to establish decent wireless networks that is why wireless engineering efforts must focus on two things:
- Wireless devices must strictly follow a common standard, IEEE 802.11.
- Wireless coverage should exist in the area where the devices are expected to use it.
Wireless networks take place over free space by communicating through Radio Frequency (RF) signals. Data should traverse in both directions to fully take advantage of wireless networking, which can be a challenge using free space.
IEEE 802.11 WLANs are always half-duplex wherein information exchange between stations uses the same frequency or channel. Only one station can transmit at any point in time, or else collisions may occur. To be able to work on full-duplex WLAN mode, the station’s transmission would have to transpire on one frequency, and it uses a different frequency to receive. Even if this is possible, the 802.11 standard does not allow full-duplex operation.
Basic Service Set (BSS)
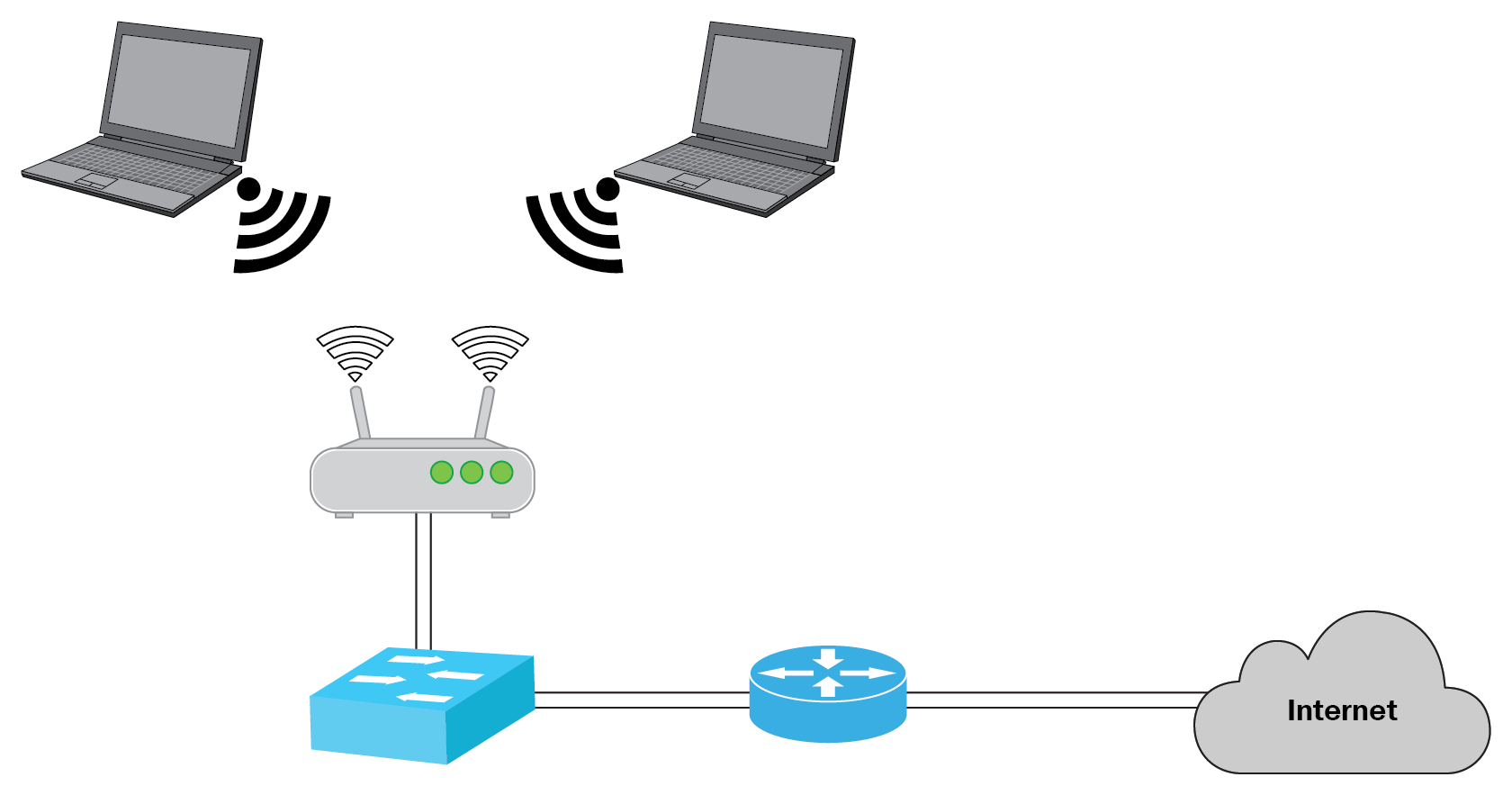
To address the limitations of wireless networks, we have to establish a Basic Service Set (BSS) and make the wireless service area a closed group of mobile devices that form around a fixed device. So that if a device wants to participate, it must first advertise its capabilities and then be granted access.
The center of a BSS is called a Wireless Access Point (WAP). The WAP functions in infrastructure mode wherein it offers services that are essential to establish wireless networks. A wireless router or access points are installed to broadcast RF signals that mobile devices can detect for them to be able to connect to their network of choice.
Types of Wireless Network
There are various types of wireless technologies that are deployed in businesses based on their capabilities and functionalities. Listed below are the different types of wireless networks and their wireless distribution method.
- Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN) – usually serves home networks that cater to a person, such as Bluetooth connectivity of a headset or wireless mouse to a laptop.
- Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) – Wireless LAN connects at least two end-devices such as laptops, mobile phones, or wireless printers via a wireless network using high-frequency signals connected to an access point which also serves as a gateway to the business network or for Internet access.
- Wireless Metropolitan Area Network (WMAN) – Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks are comparatively bigger in size than a WLAN and are deployed to connect multiple wireless local area networks that span across a small geographical area, business, or campus.
- Wireless Wide Area Network (WWAN) – this type of wireless network covers an extensive area like a state or country that contains several WMAN and WLAN in it, connecting branch offices that are separated geographically but still can be part of one network. An example of a WWAN is the mobile communications services our mobile phones use to connect to the Internet.
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training: