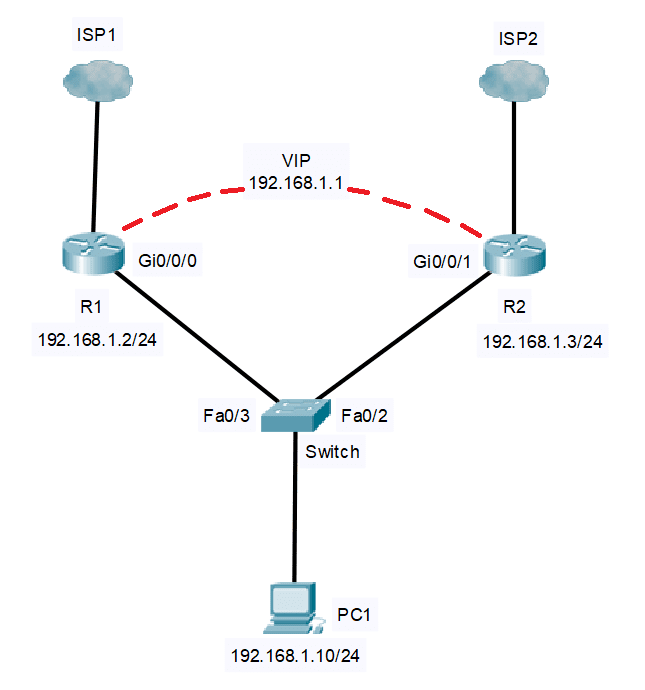
For the Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) configuration, we will use the sample network topology below. We will be configuring the routers R1 and R2 for HSRP.
R1 Configuration:
R1(config)#interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/0 R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#standby 1 ip 192.168.1.1
R2 Configuration:
R2(config)#interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 R2(config-if)#ip address 191.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 R2(config-if)#no shutdown R2(config-if)#standby 1 ip 192.168.1.1
R2 has been elected as the Active Router:
*Aug 29 04:43:24.718: %HSRP-5-STATECHANGE: Ethernet0/0 Grp 1 state Standby -> Active
R1 becomes the Standby Router:
*Aug 29 04:43:55.209: %HSRP-5-STATECHANGE: Ethernet0/0 Grp 1 state Speak -> Standby
Why is that? The priority is used to elect the Active Router and the Standby Router for an HSRP group. In case of an equal priority, the router with the highest IP address in the group will be elected as active. If there are more than two routers in the group, the second-highest IP address determines the Standby Router, and the other router or routers are in the Listen state.
If no priority is configured, the device uses the default priority of 100.
To verify the HSRP status, we can enter the ‘show standby’ command:
R2#show standby
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 - Group 1
State is Active
2 state changes, last state change 00:01:01
Virtual IP address is 192.168.1.1
Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac01
Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac01 (v1 default)
Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec
Next hello sent in 0.128 secs
Preemption disabled
Active router is local
Standby router is 192.168.1.2, priority 100 (expires in 8.624 sec)
Priority 100 (default 100)
Group name is "hsrp-Et0/0-1" (default)
Router R2 is Active. We can now see the Virtual MAC Address of 0000.0c07.ac01. Standby Router is R1, 192.168.1.2.
HSRP uses the 0000.0c07.acXX MAC address where XX is the HSRP group number.
Verify Cisco Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) Configuration
If we do ‘show interfaces GigabitEthernet 0/0/1’ from R2, we can see that the Virtual MAC Address (0000.0c07.ac01) is different from the Physical MAC Address (aabb.cc00.d000).
R2#show interfaces GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 GigabitEthernet0/0/1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is iGbE, address is aabb.cc00.d000 (bia aabb.cc00.d000) Internet address is 192.168.1.3/24
From PC1, we check the ARP cache:
C:\WINDOWS\system32>arp -a Interface: 192.168.1.10 --- 0xb Internet Address Physical Address Type 192.168.1.1 00-00-0c-07-ac-01 dynamic
We can ping the Virtual IP (VIP) from PC1:
C:\WINDOWS\system32>ping 192.168.1.1
Pinging 192.168.1.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=128ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=42ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=54ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=71ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 42ms, Maximum = 128ms, Average = 73ms
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training: