Wide Area Network (WAN) tackles the different geographical locations, such as branches on any other site or remote location, challenges that a LAN usually encounters. We are going to tackle the different network topologies that address the various situation needed by customers which the service provider provides their WAN services to interconnect their clients’ sites for a certain amount based on the requirement such as bandwidth, availability, and speed.
We will be discussing the popular WAN technology nowadays, such as Metro Ethernet (MetroE), wherein it uses physical Ethernet links to connect the customer’s network devices to the service provider’s network and other WAN topology that are used today. To be able to connect multiple sites across Wide Area Network, the service provider should be well aware of the topology to be used to address the enterprise client’s needs.
Point-to-Point
The customer basically requires basic point-to-point network connectivity between two sites separated geographically that will allow them to send and receive Ethernet frames to each other as if they are connected directly. Point-to-point topology is transparent to the customer network and acts as if there are physical connections between remote sites.
Typical dedicated leased lines connections are offered with this kind of setup, such as an E1 or T1 line. But with MetroE, service providers offer what is called an Ethernet Line Service or E-Line where two customer premise equipment (CPE) devices can exchange Ethernet frames, similar in concept to a leased line.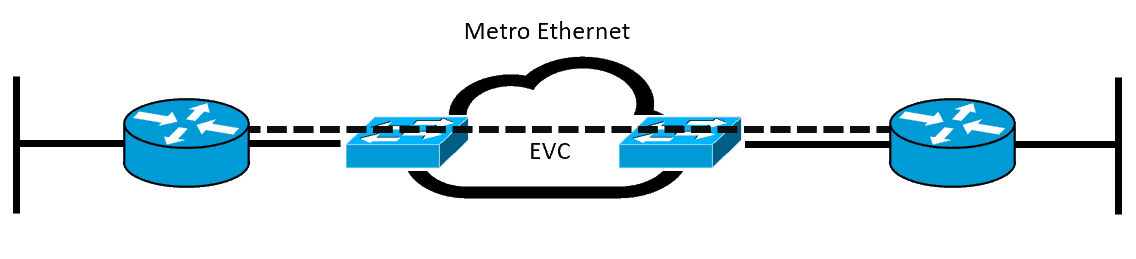
Point-to-Multipoint
This WAN topology requires a central site device that directly sends Layer 2 frames to reach remote sites, but the remote sites can only send frames to the central site. This Metro Ethernet service is known as E-Tree, wherein the central site is the E-Tree Root and the remote sites are the E-Tree leaves. This topology is also known as Hub and Spoke or partial mesh network topologies, but regardless, this type of WAN topology creates a service that addresses the need to have a hub site with several sites connected.
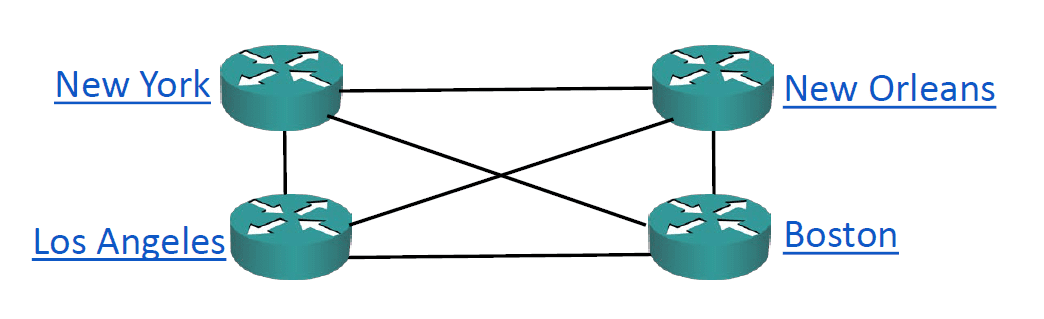
Full Mesh
Full mesh topology allows all the connected devices in the WAN topology to communicate with each other, and the people who develop MetroE has anticipated that there is a need for full-mesh connectivity of devices wherein they all send and receive Ethernet frames to each other directly without having to be dependent on a central hub. This MetroE service is called Ethernet LAN or E-LAN.
An E-LAN service permits all the devices connected to it to send frames directly to each other as if they are in one big Ethernet switch.
Ring Topology
This topology is almost like a point-to-point but is connected on both sides to provide protection just in case a fault happens. WANs that use this topology are less susceptible to failure since traffic can be routed the other way around the ring if a fault is detected on the network. But, adding new sites to the ring topology requires more work and cost compared to a simple point-to-point setup because each new site will require twice the connection needed.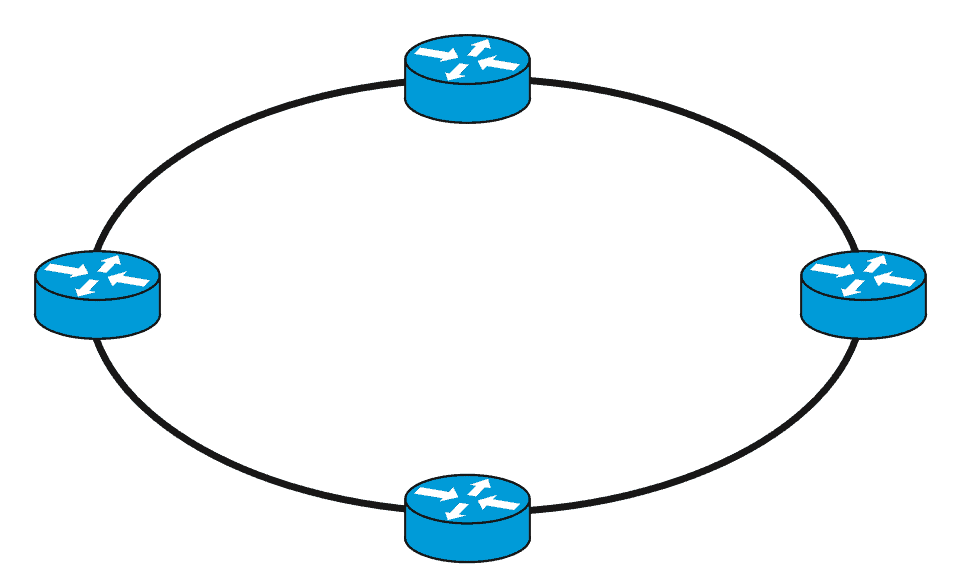
Star Topology
WAN topology using the star network configuration requires a central hub. A concentrator router is being used to ensure that data is properly sent to the destination. This topology allows easier integration of new network components to the network, which can be an important consideration for business WANs as it entails less work and cost.
This topology also makes the network less vulnerable to a single point of failure issue that may affect traffic on the network except for the central hub. The spokes have an independent link in transmitting data to the concentrator router, which means they do not depend on other spokes to function properly and can easily isolate the issue if ever something wrong happens.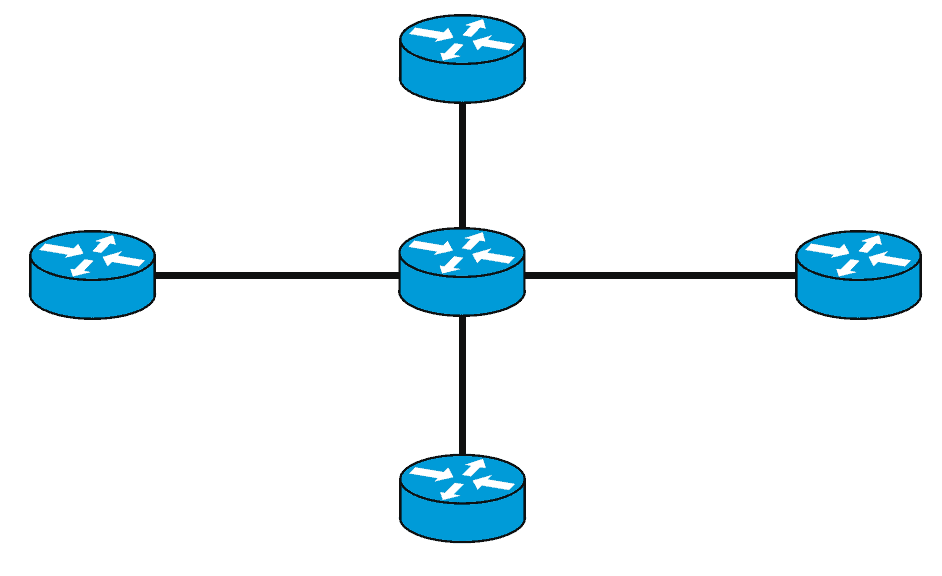
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training: