Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) is a protocol in networking that is widely used by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to provision digital subscriber line (DSL) high-speed Internet services. Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet uses standard methods of encryption, authentication, and compression specified by PPP and is defined in RFC 2516.
Obtaining IP Addresses
We don’t have to configure IP addresses manually because the ISP dynamically assigns IP addresses from its address pool to clients that are authorized to receive one. When a PPPoE session is initiated, the IP address is only used when the session is active. The IP address is released after the session is closed, allowing for efficient re-use of IP addresses.
Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet Features
Below are the features of Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE):
- Multi-Link PPPoE (MLPPP) – a unique WAN option that combines multiple PPPoE lines from the same ISP to form one larger virtual circuit.
- RADIUS Server – PPPoE server can use it to perform authentication, authorization, and accounting for access users.
- MPLS network can be set up over PPPoE interfaces.
- Data Compression – by compressing the data, the information transmitted from one user to another will become smaller, which means that the transfer of data would become faster and more efficient.
- Encryption – encrypting the data helps protect the user and the networks from malicious programs and users.
- Quality of Service (QoS) – a mechanism to control traffic and ensure the performance of critical applications, and there are certain QoS options available for the PPPoE protocol.
- Authentication Protocols:
- Password Authentication Protocol or PAP – communicates in cleartext. There’s no encryption of the information that you’re sending.
- Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol or CHAP – was created to provide additional security to this authentication process. It uses encrypted challenge to be able to send the credentials across the network.
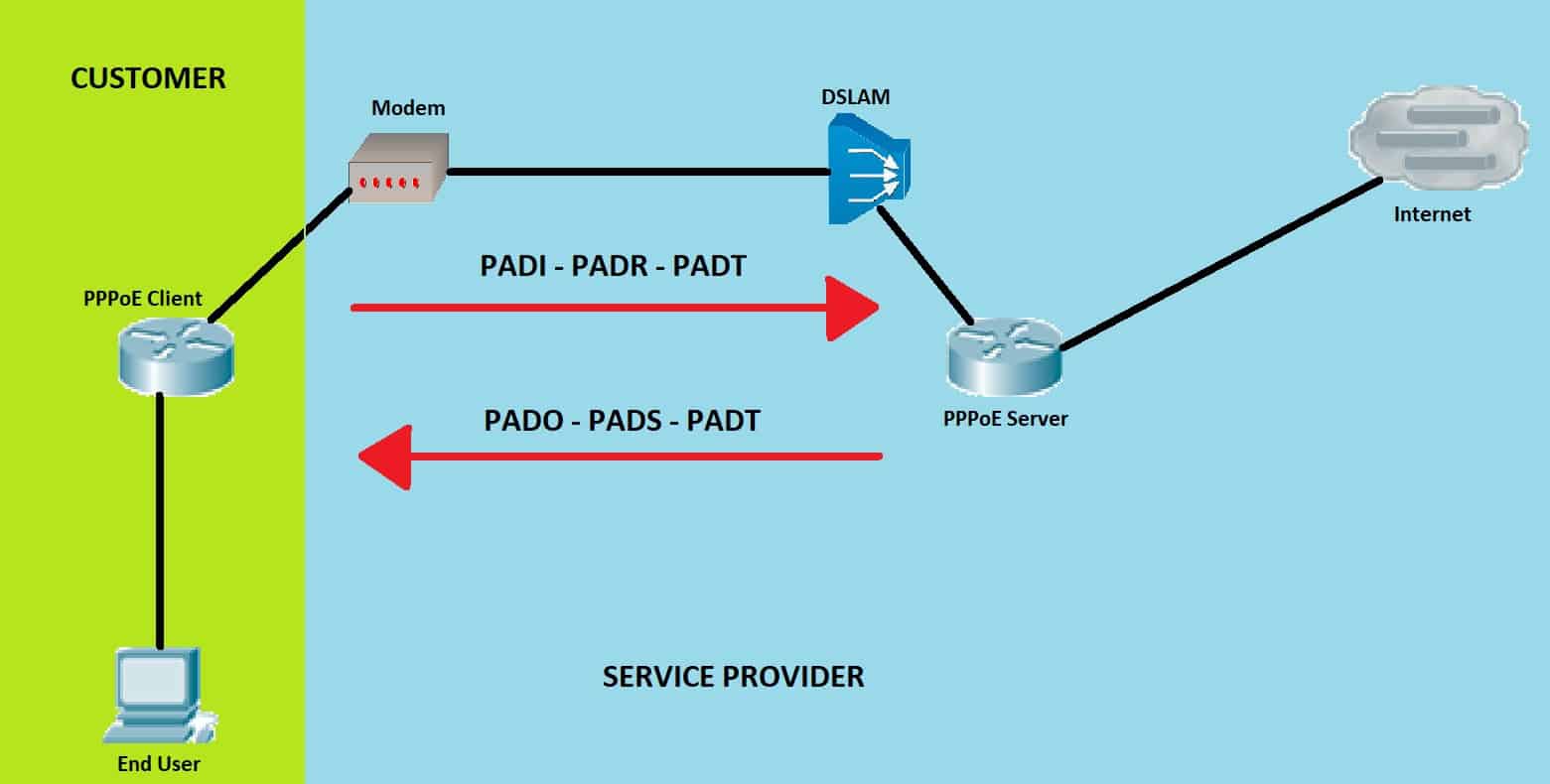
PPPoE Operation
Listed below is the sequence of how PPPOE works:
PPPoE Active Discovery Initiation (PADI) – Client sends PADI frame via layer 2 broadcast.
PPPoE Active Discovery Offer (PADO) – Server replies with its MAC Address, name, and the name of the service.
PPPoE Active Discovery Request (PADR) – Client confirms acceptance of the offer of a PPPoE connection made by the server.
PPPoE Active Discovery Session-confirmation (PADS) – Server confirms PADR and replies with PADS containing a session ID. The connection has now been fully established.
PPPoE Active Discovery Termination (PADT) – This Ethernet frame terminates the PPPoE connection and can be initiated from either the client or the server side.
PPPoE vs DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a protocol for obtaining IP addresses from DHCP servers, while Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet is a method of connecting to an ISP.
DHCP configuration is very popular and is widely used, while PPPoE is slowly falling out of favor.
You would need to have the correct credential (username and password) with PPPoE, while the configuration on the DHCP client is automatic.
Originally, routers were designed either to handle Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet connections or DHCP connections but not both. Today, most routers are capable of handling either type of connection.
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training: