Organization before was using only physical network devices, like routers and switches, and physical servers to host their applications located on their premise. That approach is costly in terms of implementation and maintenance, and it is not scalable if you want to upgrade the devices as it requires a lot of effort. Nowadays, physical network devices and servers in organizations are slowly shifted into the cloud because of known disadvantages on an on-premise architecture. The public cloud providers now offer different service models, namely, IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is an on-demand availability of computer resources like server storage and cloud computing power provided by public cloud providers like Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services. It enables us to use cloud computing resources that are distributed on multiple data centers. Each data center is located in a different location to provide the highest redundancy, availability, and disaster recovery of cloud computing resources.
Cloud Computing Service Models
Cloud computing providers offer three cloud computing services in which consumers can use. Thse are IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. We will discuss these services in detail.
1. Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
IaaS offers cloud services such as storage, compute, and networking resources on a pay-as-you-go basis within a virtualized environment. It provides the consumers more control over physical hardware and software resources by allowing them to modify storage containers, modify CPU and RAM, and configuring network resources within the cloud platform.
IaaS simplifies the deployment of servers and network devices by deploying virtual machines, and virtual routers, firewalls, switches, and other virtual appliances found in public cloud providers platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and GCP.
2. Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers a complete cloud platform like hardware, software, and infrastructure for running, managing, and developing software applications that software developers are using. Compared to the on-premises platforms, PaaS is easy to deploy, scalable, and flexible in terms of building and maintaining it. It is designed to allow consumers to access any underlying applications like application development environment and programming frameworks.
With this platform, the consumer has more control over the working environment as compared to IaaS that deploys only basic operating systems like Linux Red Hat or Microsoft Windows. PaaS service is somewhat the same as IaaS as consumers can also deploy and configure VM, CPU, RAM, storage, and other virtual appliance. The main difference between them is that PaaS offers more software tools used in the management and development of software applications.
3. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
SaaS providers offer software or application on a subscription basis that is hosted on the cloud. The consumer is only provided with the application’s user interface, and applications are not installed on the user’s device. One common example of SaaS applications is Google Suite and Office 365 applications, in which users can access the applications like emails and Google Docs using a web browser. In SaaS, users are not concerned about the underlying infrastructure that their application is hosted as the SaaS providers are responsible for maintaining the underlying software and hardware of the application.
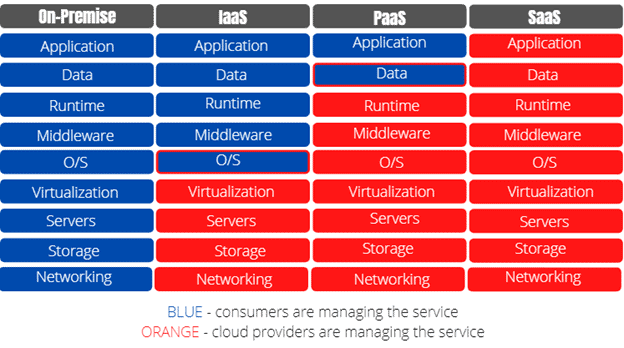
On-Premise vs. IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS
The snippet below shows us the summary of the services offered on-premise and the cloud providers’ IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS services.
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training: