This topic is not included in the latest version of the CCNA exam (200-301). If you are studying for the exam feel free to skip this article.
Each VLAN is its own subnet and broadcast domain, which means that frames broadcasted onto the network are switched only between the ports within the same VLAN. For interVLAN communication, an OSI layer 3 device (usually a router) is needed. This layer 3 device needs to have an IP address in each VLAN and have a connected route to each of those subnets. The hosts in each subnet can then be configured to use the router’s IP addresses as their default gateway.
Three options are available for routing between VLANs:
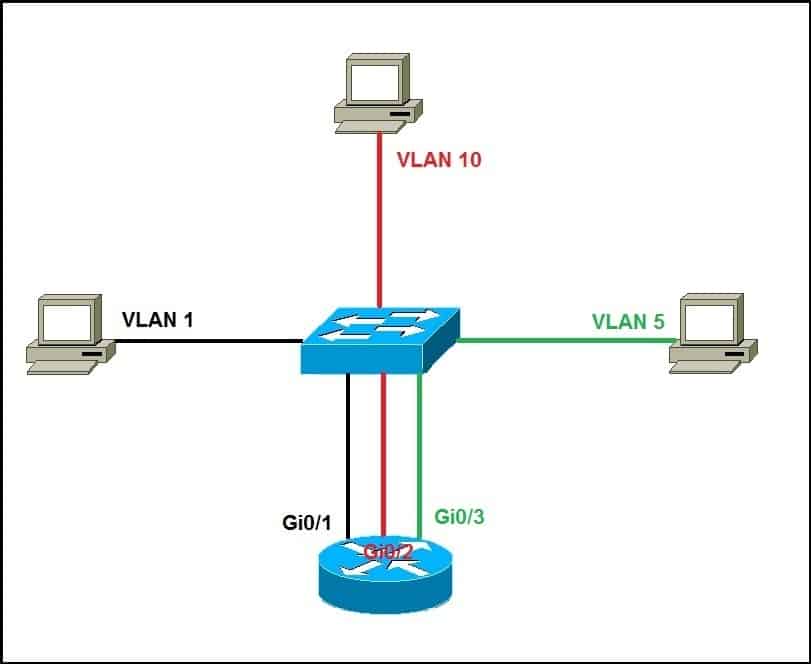
1. Use a router, with one router LAN interface connected to the switch for each VLAN. Since you need one Ethernet interface on your router to connect to each VLAN, this option is not really scalable and rarely used today.
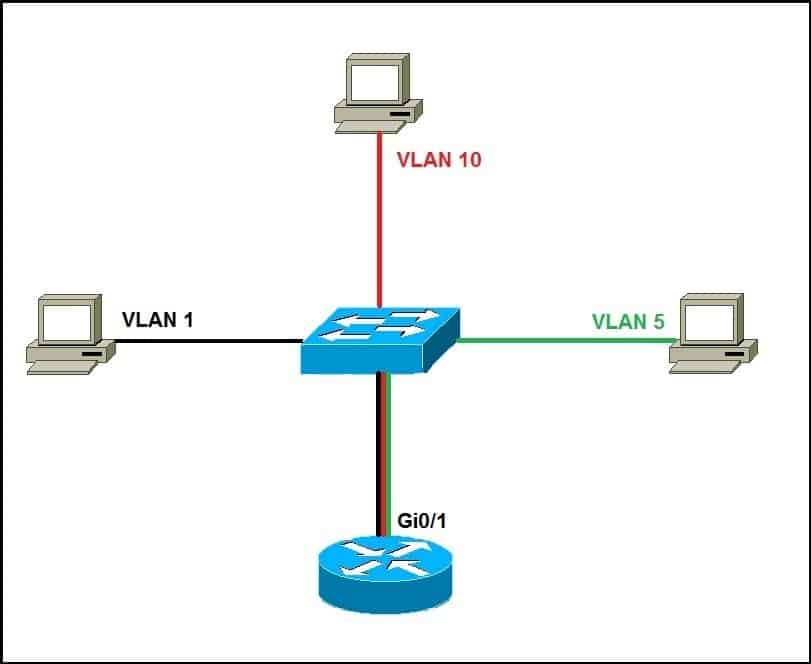
2. Use one router interface with trunking enabled. This option is called router on a stick (ROAS) and enables all VLANs to communicate over a single interface.
3. Use a Layer 3 switch, which is a device that performs both the switching and routing operations.
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training: