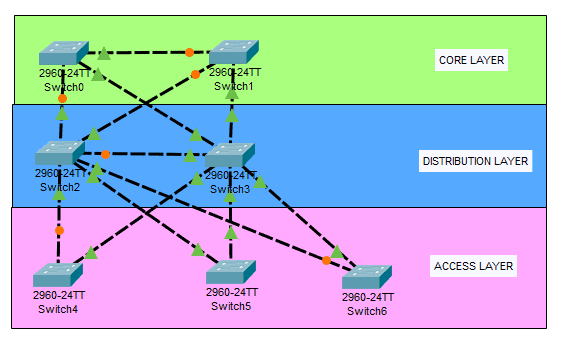
Spanning Tree Protocol is a Layer 2 loop prevention mechanism that will block one port on the network switch if it detects a loop of broadcast messages within its architecture. By default, spanning trees are enabled on most interconnected Cisco switches. Switches send out Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) on all active interfaces. BPDU contains STP information needed to elect a root switch and detect loops.
STP Root Bridge Election
The switch assigns a root bridge within the interconnected switches. A root bridge is the central point of all switches and will be responsible for forwarding the traffic. The switch selects a root bridge by using the switch priority and the MAC address. Each switch has its own bridge ID and has a default priority value of 32768. The root bridge is taking precedence over the MAC address. If a switch has the lowest bridge priority value among the switches within the LAN, then it will be elected as the spanning tree root bridge.
If all the spanning tree bridge priority has the same priority value on all the switches, then the MAC address will be the tiebreaker. The lowest MAC address will be elected as the Root Bridge. Most of the older switches have a lower value of MAC address and have lower bandwidth and limited CPU/memory as compared to newer switches. Electing an older switch as the root bridge will cause a suboptimal operation on your network.
Spanning Tree Priority Root Bridge Optimization
We should avoid electing a root bridge using the MAC address, which can cause a suboptimal network performance as it will choose the oldest switch with the lowest MAC address in the network. The example spanning tree topology below shows the LAN switches that elect Switch6 as the Root Bridge by using the MAC address election. Let’s assume that Switch6 is the oldest switch in the group. All traffic will go and process first on Switch6 before it goes to the destined switch. That will create a poor performance of the network.
To prevent having a suboptimal network, we need to manually choose a root bridge within the network. By doing that, we need to manually configure a value of the root bridge or manually assign it as a root bridge by using the ‘root primary’ command. This will set the bridge priority to 24576, which is lower than the default priority.
What if the primary root bridge fails? To optimize further, we need to assign the other core switch as the secondary root bridge in case the primary root bridge is not operational. To do that, we enter the ‘root secondary’ command. This will set the bridge priority to 28672, which is lower than the default priority but higher than the root primary. When the primary switch fails, the switches will elect a new root bridge. It will then failover to the secondary switch, and it will be elected as the new root bridge.
STP Root Primary and Root Secondary Configuration
Based on the diagram above, we need to manually configure the core switch as the root bridge as they have higher bandwidth and better features in general as compared to the other switches on the group. The below configuration shows how we configure the core switch, Switch0, as the root bridge.
Switch0(config)#spanning-tree vlan 1 root primary
To verify, we can use the ‘show spanning-tree’ command.
Switch0#show spanning-tree vlan 1 VLAN0001 Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee Root ID Priority 24577 Address 0001.9725.3338 This bridge is the root Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority 24577 (priority 24576 sys-id-ext 1) Address 000.19725.3338 Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Below is the configuration to assign Switch1 as the secondary root.
Switch1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 1 root secondary
Again, we can use the ‘show spanning-tree’ command to verify our configuration.
Switch1#show spanning-tree vlan 1 VLAN0001 Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee Root ID Priority 24577 Address 0001.9725.3338 Cost 19 Port 1 (FastEthernet0/1) Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority 28673 (priority 28672 sys-id-ext 1) Address 0040.0B2C.E63A Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 20
The spanning tree port priority value can also be changed to improve the effectiveness of STP.
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training: