IPv4 or Internet Protocol version 4, address is a 32-bit string of numbers separated by periods. It uniquely identifies a network interface in a device. IP is a part of the TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) suite, where IP is the principal set of rules for communication on the Internet. An IP address is needed to be allocated on the devices, such as PCs, printers, servers, routers, switches, etc., to be able to communicate with each other in the network and out the Internet.
IPv4 Address Format
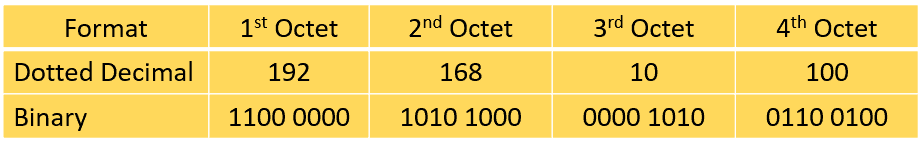
IPv4 addresses are expressed as a set of four numbers in decimal format, and each set is separated by a dot. Thus, the term ‘dotted decimal format.’ Each set is called an ‘octet’ because a set is composed of 8 bits. The figure below shows the binary format of each octet in the 192.168.10.100 IP address:
A number in an octet can range from 0 to 255. Therefore, the full IPv4 address space goes from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255. The IPv4 address has two parts, the network part and the host part. A subnet mask is used to identify these parts.
Network Part
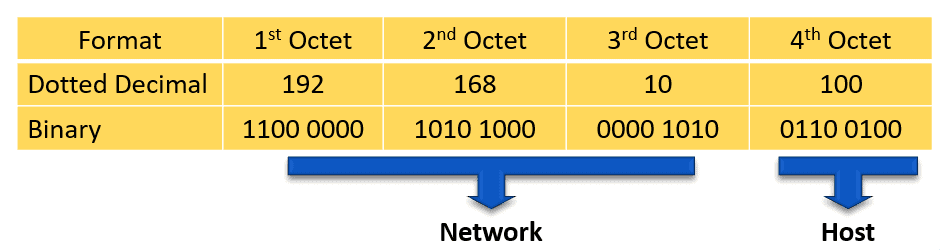
The network part of the IPv4 address is on the left-hand side of the IP address. It specifies the particular network to where the IPv4 address belongs. The network portion of the address also identifies the IP address class of the IPv4 address.
For example, we have the IPv4 address 192.168.10.100 and a /24 subnet mask. /24 simply means that the first 24 bits, starting from the left side, is the network portion of the IPv4 address. The 8 remaining bits of the 32 bits will be the host portion.
Host Part
The host portion of the IPv4 address uniquely identifies the device or the interface on your network. Hosts that have the same network portion can communicate with one another directly, without the need for the traffic to be routed.
IPv4 Address Allocation
The Internet Protocol address can be allocated to hosts or interfaces either manually or dynamically.
- Static – static IP address is set manually on the device. It is best practice to set static IP addresses on network devices, such as routers and switches, and on servers as well.
- Dynamic – dynamic IP address can be automatically allocated to a device via Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). Dynamic IP addresses are best to be used on end devices, such as PCs.
Types of IPv4 Addresses
We have two types of IP addresses, namely public IP addresses and private IP addresses.
- Public IP address – used to route Internet traffic. This is used on the Internet and is given out by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to their customers.
- Private IP address – used in private networks for internal traffics within the LAN. Private addresses are not routable out the Internet.
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest-rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training: