HSRP, or Hot Standby Router Protocol, is one of the commonly used First Hop Redundancy Protocols (FHRP). We also have Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) and Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP).
HSRP is a Cisco proprietary redundancy protocol that allows failover of the next-hop IP device. It operates with an Active-Standby Model where only one device is supporting end-user traffic at any time, and the other device is on standby waiting to take over should the active device fails.
One major factor that network architects or engineers consider when designing a network is high availability (HA) and avoiding a single point of failure (SPOF). It’s important, especially for critical operations like healthcare, emergency, government, and banking services.
How Does HSRP Work?
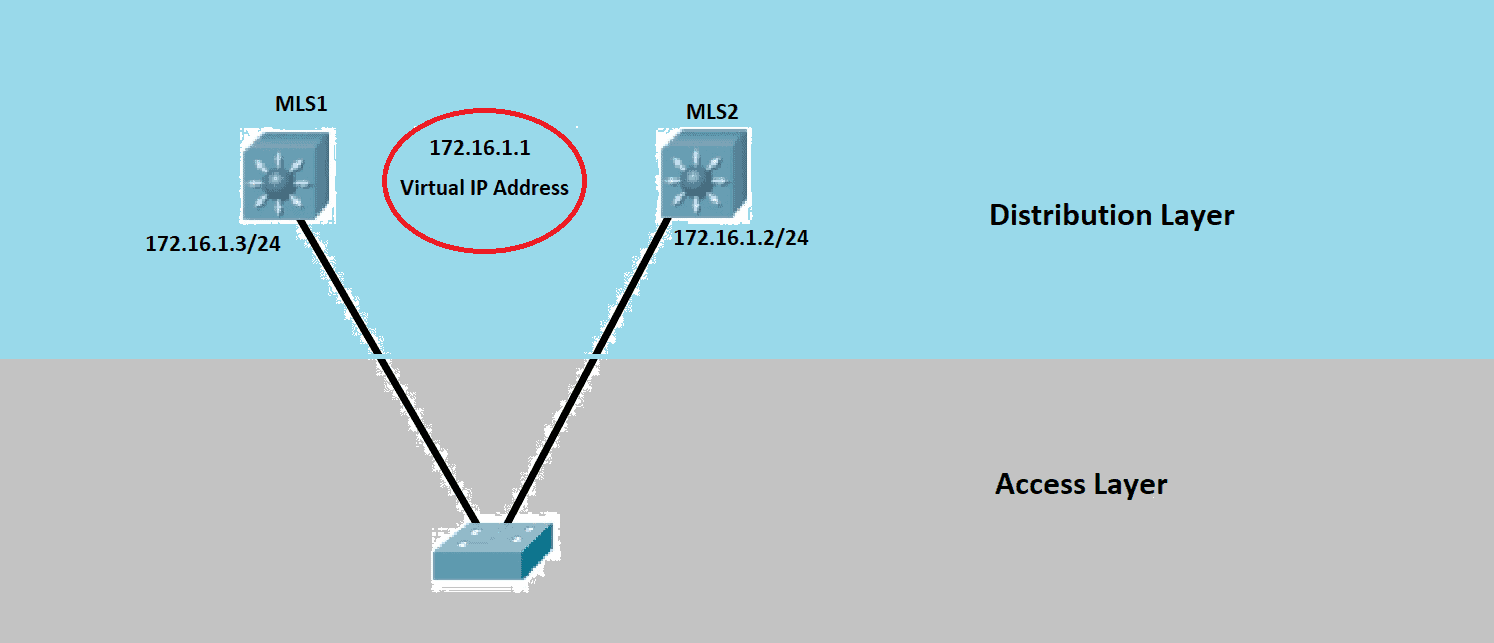
In our example above, we have two Layer 3 Cisco Switches in our Distribution Layer, MLS1 and MLS2. Behind these Layer 3 Switches is our Access Layer Switch, where our end-user connects to. If either L3 Devices or physical links fail, we need a dynamic way to failover our traffic from MLS1 to MLS2, and HSRP will take care of it.
Once we configure HSRP on the L3 devices, it elects the Active Router based on the higher priority. If both routers have default priority, the router with the higher HSRP interface IP Address becomes the Active Router.
If no priority is configured, it uses the default of 100.
For the configuration, we need to specify the HSRP Virtual IP address (VIP), which should be on the same subnet as the HSRP interfaces. You cannot set the physical IP as VIP. After the election, the Active Router implements the VIP and the virtual MAC Address and starts responding to ARP requests from the hosts.
HSRP’s virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.acXX, where XX is the HSRP group number.
HSRP Messages
With HSRP, there are three types of multicast messages sent between the devices:
Hello – sent between Active and Standby devices every 3 seconds by default. If MLS2 does not hear from MLS1 in 10 seconds, MLS2 will take over the active role.
Resign – sent by the active device when it’s going offline or ready to give up the active role for some other reason. This message tells MLS2 to be ready and take over the active role.
Coup – used when a standby router wants to assume the active role (preempt).
The command to configure a preempt delay in HSRP is:
(config-if)# standby <HSRP group> preempt delay minimum <0-3600>
HSRP States
Listed below are the different Hot Standby Router Protocol states:
Initial – when the link comes up.
Learn – the HSRP device is trying to learn VIP.
Listen – the device knows the VIP and listens for hello messages from other HSRP devices.
Speak – the device sends hello messages and participates in the election to become the active router.
Standby – the device is patiently waiting to take over should the active router fails.
Active – the device receives the data intended for VIP.
Here are some additional features about HSRP Version 1 and Version 2:
| Version 1 | Version 2 | |
| Group Numbers | 0 – 255 | 0 – 4095 |
| Virtual MAC Address | 0000.0c07.acXX (XX = group number) | 0000.0c9f.fXXX (XXX = group number) |
| Multicast Address | 224.0.0.2 | 224.0.0.102 |
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training: