The term local area network (LAN) is commonly used to describe a network of devices in a limited area (a house, office, building, etc.). This type of network is usually capable of achieving high data transfer rate (up to 10 Gbps!) at low cost. Examples of this type of network are a small office network inside a single building or your home network.
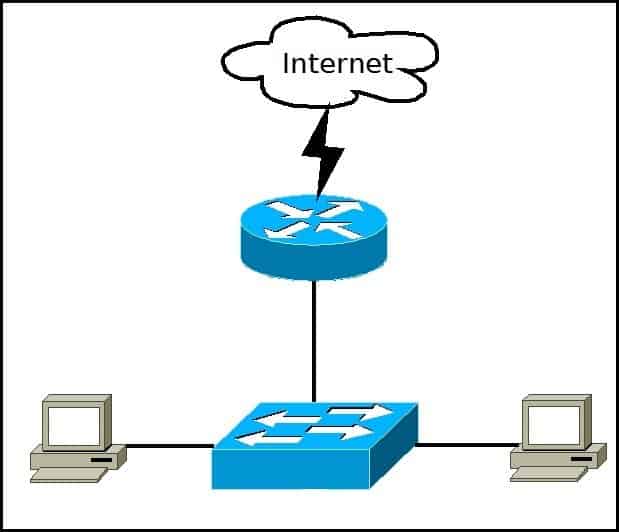
A typical SOHO (small office/home office) LAN consist of PCs, printers, switches, routers, and cabling that connects all these devices together. The following figure shows a typical LAN:
In the picture above we have two computers that are connected to a switch. The switch is then connected to a router that provides the LAN with access to the Internet.
Some of the most popular LAN technologies are Ethernet, Token Ring and FDDI. Most LAN networks use TCP/IP to communicate. Twisted-pair cabling is usually used in a LAN.
Ethernet is by far the most popular wired LAN technology. It defines wiring, signaling, connectors, frame formats, protocol rules, etc. Most modern LANs also support the wireless LAN (WLAN) technology, defined by the IEEE 802.11 standards. WLANs use radio waves instead of wires or cables for links between devices.
The term metropolitan area network is used to describe a network in a single metropolitan area, hence the name. This type of network is usually bigger than a LAN and smaller than a WAN. An example of this type of network would be a network that connects two company offices inside the same city.
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training: