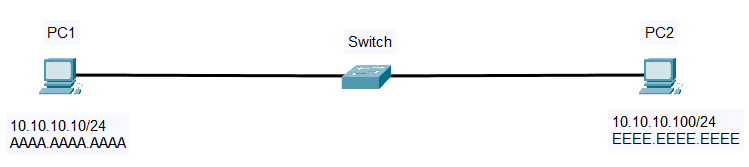
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a Layer 2 protocol that maps an IP address (Layer 3) to a MAC address (Layer 2). So, how does the traditional ARP work? In this example, PC1 wants to communicate with PC2. PC1 knows the destination IP address but not the destination MAC address.
The ARP process will be as follows:
1. First, PC1 checks its ARP table for PC2’s IP address (10.10.10.100).
2. If there is no cache, PC1 will send ARP Request, a broadcast message (source: AAAA.AAAA.AAAA, destination: FFFF.FFFF.FFFF) to all hosts on the same subnet.
3. All hosts will receive the ARP Request, but only PC2 will reply. PC2 will send an ARP Reply containing its own MAC address (EEEE.EEEE.EEEE).
4. PC1 receives the MAC address and saves it to its ARP Table.
Why Do We Need Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI)?
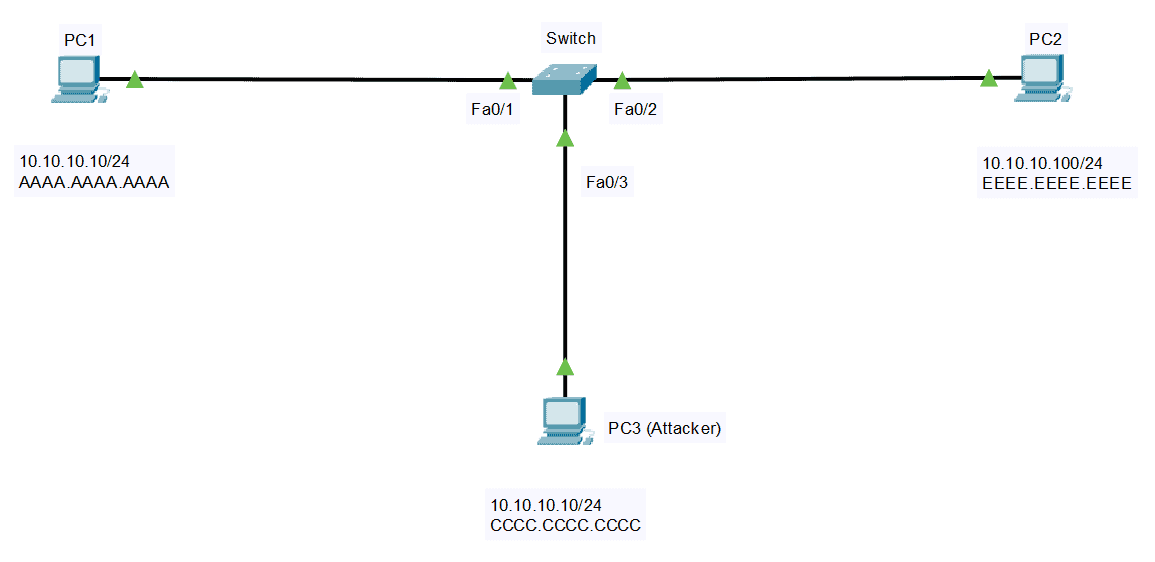
You may be asking why we need Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI). In our first example, a rogue peer, PC3, is connected to one of the switch ports. PC3 can send a Gratuitous ARP or an ARP Reply that was not prompted by an ARP Request to update the ARP mapping of the other hosts on the network.
Unknowingly, PC2 will update its ARP Cache and change the MAC address of PC1 to the MAC address of PC3. Same with the other direction, PC3 can spoof PC2 by lying about its MAC address. This attack, or ARP spoofing, is also called a Man-in-the-Middle attack.
PC2’s ARP Cache before spoofing:
C:\>arp -a Internet Address Physical Address Type 10.10.10.10 aaaa.aaaa.aaaa dynamic
PC2’s ARP Cache after spoofing:
C:\>arp -a Internet Address Physical Address Type 10.10.10.10 cccc.cccc.cccc dynamic
How Does DAI Prevent a Man-in-the-Middle Attack?
With Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI), the switch compares the incoming ARP packet and should match entries in:
1. DHCP Snooping Binding Table
2. Any configured ARP ACLs (can be used for hosts using static IP instead of DHCP)
If the ARP and any of the above do not match, the switch discards the ARP message.
Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) Configuration
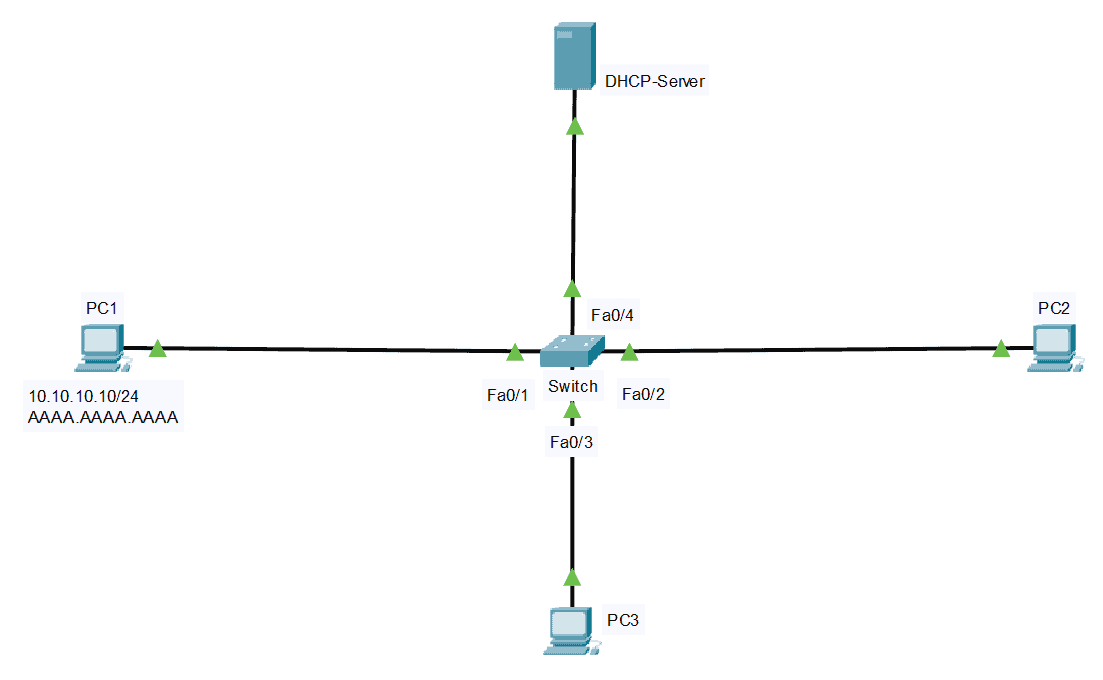
For our Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) configuration example, the switch ports are all under VLAN 100.
To enable Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) on VLAN 100:
Switch#conf t Switch(config)#ip arp inspection vlan 100
To enable Interface Trust State:
Switch(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/4 Switch(config-if)#ip dhcp snooping trust
To bypass the Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) process, you will usually configure the interface trust state towards network devices like switches, routers, and servers under your administrative control.
We can also use the ‘show ip arp inspection’ command to verify the number of dropped ARP packets:
Switch#show ip arp inspection
In our example, if we want to configure PC1 with static IP instead of DHCP, we must create a static entry using ARP ACL.
Switch(config)#arp access-list PC1-Static Switch(config-arp-nacl)#permit ip host 10.10.10.10 mac host aaaa.aaaa.aaaa Switch(config)#ip arp inspection filter PC1-Static vlan 100
Now, the switch will check the ARP access list first, and then when it doesn’t find a match, the switch will check the DHCP Snooping Binding Table.
An attacker could also generate a large number of ARP messages, causing CPU overutilization in the switch (Denial-of-Service or DoS). Note that DAI works in the switch CPU rather than in the switch ASIC. We can prevent this type of attack by limiting DAI Message Rates.
Configuring ARP Inspection Message Rate Limits
An untrusted interface allows 15 ARP packets per second by default. Here’s how we can change it:
Switch(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/1 Switch(config-if)#ip arp inspection limit rate 8 burst interval 4
This interface now only allows 8 ARP packets every 4 seconds.
We can verify this with the following command:
Switch#show ip arp inspection interfaces Interface Trust State Rate (pps) Burst Interval --------------- ----------- ---------- -------------- Fa0/1 Untrusted 8 4 Fa0/2 Untrusted 15 1 Fa0/3 Untrusted 15 1
Dynamic ARP Inspection is an excellent security feature, but before configuring DAI, we need to think and make a few decisions based on our goals, topology, and device roles. We do not want to block important traffic after enabling it.
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training: