There are different WAN connectivity options between the client and the cloud service provider. We will discuss the public cloud deployment model more since the on-premises cloud does not need interconnections since all the infrastructure is within the enterprise network.
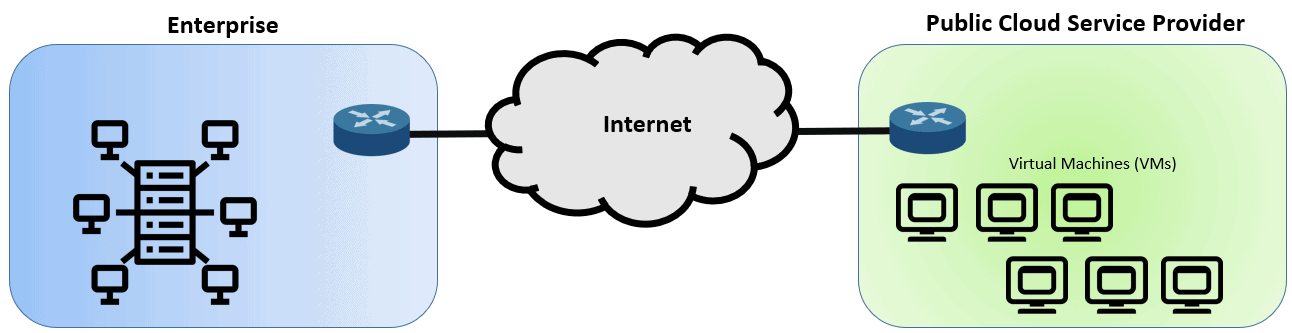
Enterprise WAN to Cloud via the Internet
Imagine a business having to operate without using a cloud. All the applications needed are stored in a data center which is expensive to maintain and put up, and access to it is tedious. So connecting your enterprise network and the public cloud via the Internet is one of the fastest and most cost-effective ways of connecting your end-users and the cloud service the enterprise needs.
Pros and Cons in Connecting to Public Cloud with Internet
Connecting to the public cloud via the Internet can have its benefits and disadvantages. An advantage is that both the customer and cloud providers have an Internet connection, so they can access cloud services easily. Below are some excellent reasons to utilize the Internet as the WAN connection to the public cloud service:
- Agility – the ability to be able to have public cloud connectivity as long as there is an Internet connection.
- Migration – transferring the workload from one cloud provider to another can be easy because all cloud providers have direct access to the Internet.
- Distributed users – users who are part of the enterprise can easily access the public cloud given that they have Internet on their devices.
However, using the Internet as the connectivity option between the WAN and Internet also has its downside. The Internet is indeed a quick fix since it is already readily available, but going that route also means that there is not much planning has been done upon deployment of the public cloud service. With a small amount of time dedicated to planning, the enterprise takes some risks that may affect the business.
Here are some of the disadvantages that should be considered before deciding on having direct cloud connectivity via the Internet.
- Security – obviously, the Internet is comparably less secure than a Private WAN and always has the higher risk of exposing your sensitive data to the dreaded so-called “man in the middle”.
- Capacity – as the enterprise expands, so does the network traffic, and capacity is one thing that should be considered when choosing the Internet as your cloud connection to the WAN.
- Quality of Service (QoS) – the Internet has no assurance regarding QoS, unlike private WANs. This means using the Internet has a greater risk of a worse user experience than what is expected because of higher latency, jitter, and packet loss.
- No WAN SLA – network service providers usually do not have service-level agreements for WAN performance via the Internet.
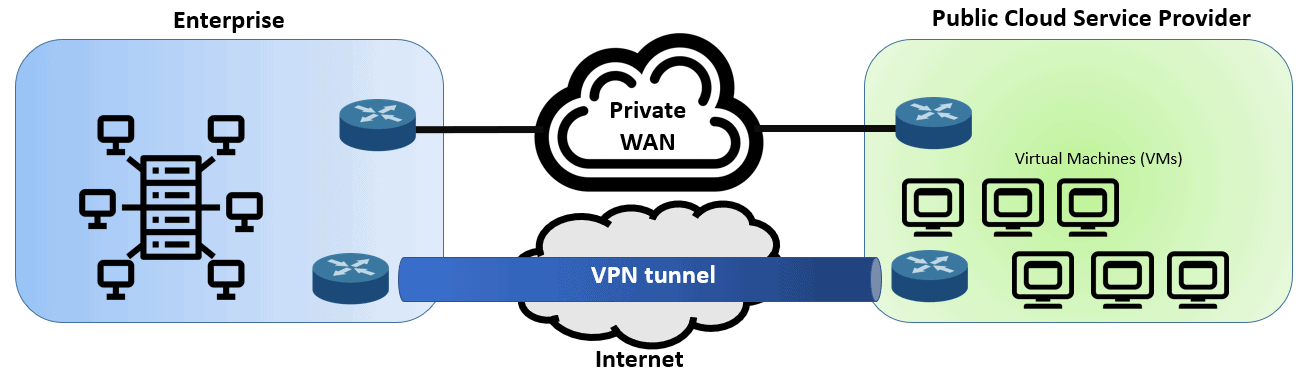
Private WAN and Internet VPN Access to Public Cloud Connectivity
As defined by the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), one criterion of cloud computing is that it has to have broad network access. In public clouds, that means supporting different WAN connectivity options. Let us discuss the two most used categories: Private WAN and Internet VPN tunnel.
Cloud service providers have offered VPN tunnels via the Internet to their clients while the enterprise configures the matching VPN service on one of its own routers. The customer can also utilize its own router within the cloud service – a virtual router, running as a virtual machine and configure VPN services on that router.
Private WAN connections require planning the physical infrastructure. Larger public cloud service providers own multiple cloud data centers spread worldwide that already have established dedicated connectivity to major WAN services that help them create a private WAN connection to their customers. Here are some of the major public cloud companies;
- Amazon Web Services
- Google Cloud
- Microsoft Azure
- Rackspace
Pros and Cons of Private WAN to Public Cloud Connectivity
We need to look at the following considerations when using Private WAN as a solution for enterprise WAN connectivity to the public cloud:
Pros:
- Security
- QoS
- Capacity
Cons:
- Mandatory requirement of planning
- Time-consuming
- Cost
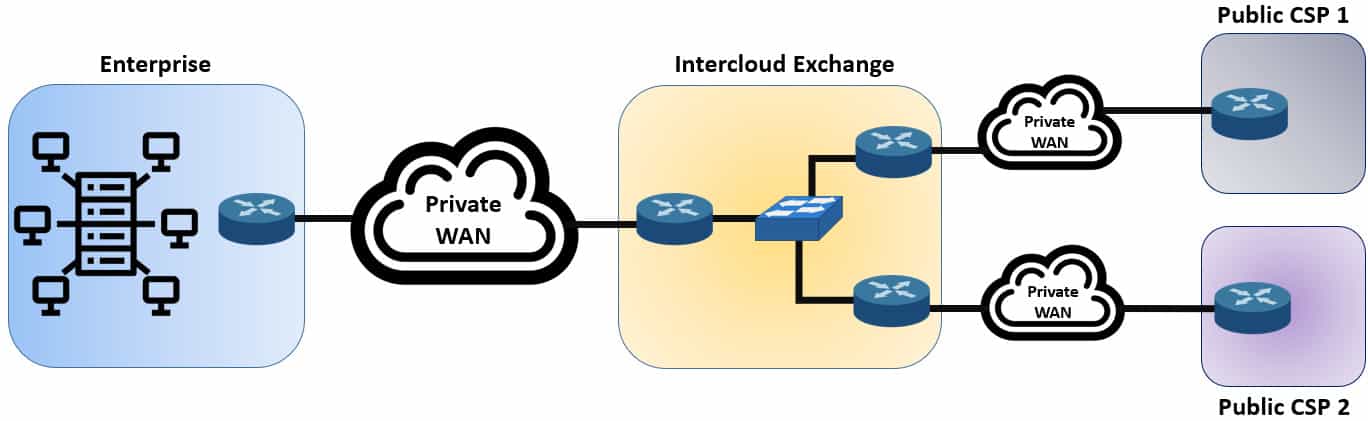
Intercloud Exchange
Public cloud computing has been a competitive market for multiple cloud providers, which gives the customers many options to have their money’s worth. Whenever a cloud consumer decides to transfer from one cloud service provider to another, the tedious workload of migrating all your traffic can be really a challenge and time-consuming. A solution to address this problem is called intercloud exchange (or simply an intercloud).
Basically, an intercloud is a company that offers a private network as a service to the consumers. It has already established connectivity with multiple public cloud providers. Once connected, the cloud services that the cloud customer needs can be configured to their preferred cloud service provider, and if ever they need to migrate to another, the intercloud will have to just reconfigure the network connectivity to the new private WAN.
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training: