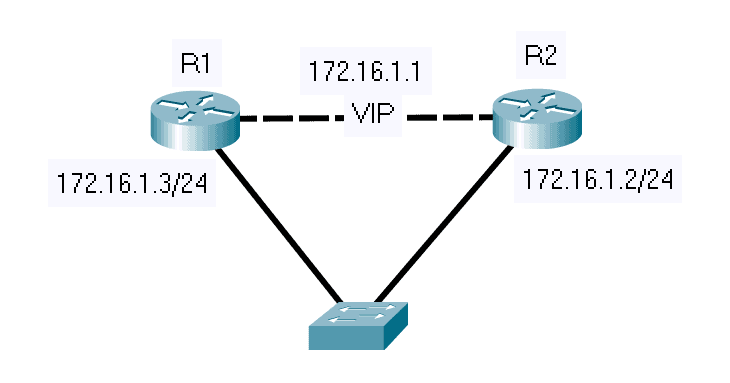
If we want a specific router to always assume the role of an Active HSRP Router whenever it’s up and running, Then, we can use HSRP Preempt. Preemption is important if we have routers with bigger resources, higher bandwidth, or less latency over the other routers in our network.
Unlike Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP), where preemption is enabled by default, with Cisco Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP), we need to set the ‘standby preempt’ command in order to allow the router with the higher HSRP priority level to immediately assume Active status whenever it’s up. The default priority is 100, but we can change the priority value to manipulate the election process.
The Three HSRP Message Types
The HSRP router can send three message types:
Hello – is sent between the Active router and the Standby router every 3 seconds by default. In our example network diagram below, if router R2 does not hear from router R1 in 10 seconds, R2 will take over the active role.
Resign – is sent by the active router or device when it’s going offline or ready to give up the active role for some other reason. This message tells router R2 to be ready and take over the active role.
Coup – is used when a standby router wants to assume the active role (preempt).
HSRP Preempt Configuration
Using the same network diagram above as our example, below are the HSRP configuration commands for enabling preemption in our Layer 3 devices, such as routers and layer 3 switches. By entering the ‘standby preempt’ command, we are able to set a router to an active state immediately.
R1:
R1#conf t R2(config)#interface FastEthernet0/1 R1(config-if)#ip address 172.16.1.3 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#standby 10 preempt R1(config-if)#standby 10 ip 172.16.1.1 R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#end
R2:
R2#conf t R2(config)#interface FastEthernet0/1 R2(config-if)#ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0 R2(config-if)#standby 10 priority 90 R2(config-if)#standby 10 ip 172.16.1.1 R2(config-if)#no shutdown R2(config-if)#end
Verifying HSRP Preemption
Let us verify the HSRP status of our router by issuing the ‘show standby‘ command in the privileged exec mode:
R1#show standby FastEthernet0/1 - Group 10 State is Active 2 state changes, last state change 00:03:46 Virtual IP address is 172.16.1.1 Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac0a Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac0a (v1 default) Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec Next hello sent in 0.512 secs Preemption enabled Active router is local Standby router is 172.16.1.2, priority 90 (expires in 8.336 sec) Priority 100 (default 100) Group name is "hsrp-Fa0/1-10" (default)
We can see that R1 was elected as the Active Router. The Virtual IP (VIP) is 172.16.1.1, the virtual MAC Address is 0000.0c07.ac0a, and preemption is enabled. On the other hand, R2 acts as a Standby Router.
R2#show standby FastEthernet0/1 - Group 10 State is Standby 1 state change, last state change 00:02:40 Virtual IP address is 172.16.1.1 Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac0a Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac0a (v1 default) Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec Next hello sent in 1.200 secs Preemption disabled Active router is 172.16.1.3, priority 100 (expires in 10.192 sec) Standby router is local Priority 90 (configured 90) Group name is "hsrp-Fa0/1-10" (default)
Let’s shut down router R1’s Fa0/1 interface and see what happens.
R1(config-if)# *Sep 4 17:42:04.003: %HSRP-5-STATECHANGE: FastEthernet0/1 Grp 10 state Active -> Init R2# *Sep 4 17:42:04.002: %HSRP-5-STATECHANGE: FastEthernet0/1 Grp 10 state Standby -> Active
Now, R2 assumes an active HSRP router role.
R2# show standby FastEthernet0/1 - Group 10 State is Active 2 state changes, last state change 00:01:56 Virtual IP address is 172.16.1.1 Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac0a Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac0a (v1 default) Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec Next hello sent in 2.288 secs Preemption disabled Active router is local Standby router is unknown Priority 90 (configured 90) Group name is "hsrp-Fa0/1-10" (default)
Let’s try to enable R1’s Fa0/1 interface and see if the higher priority router preempts the lower priority router and becomes the active router.
R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)# *Sep 4 17:45:06.990: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up *Sep 4 17:45:07.994: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up R1(config-if)# *Sep 4 17:45:08.040: %HSRP-5-STATECHANGE: FastEthernet0/1 Grp 10 state Listen -> Active
There you go, R1, the higher priority router, becomes the active HSRP router again.
R1#show standby FastEthernet0/1 - Group 10 State is Active 4 state changes, last state change 00:01:04 Virtual IP address is 172.16.1.1 Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac0a Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac0a (v1 default) Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec Next hello sent in 0.064 secs Preemption enabled Active router is local Standby router is 172.16.1.2, priority 90 (expires in 9.520 sec) Priority 100 (default 100) Group name is "hsrp-Fa0/1-10" (default)
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training: