STP uses the Spanning-Tree Algorithm (SPA) to create a topology database of the network. To prevent loops, SPA places some interfaces in forwarding state and other interfaces in blocking state. How does STP decides in which state the port will be placed? A couple of criteria exist:
1. all switches in a network elect a root switch. All working interfaces on the root switch are placed in forwarding state.
2. all other switches, called nonroot switches, determine the best path to get to the root switch. The port used to reach the root switch (root port) is placed in forwarding state.
3. on the shared Ethernet segments, the switch with the best path to reach the root switch is placed in forwarding state. That switch is called the designated switch and its port is known as the designated port.
4. all other interfaces are placed in blocking state and will not forward frames.
STP considers only working interfaces – shutdown interfaces or interfaces without the cable installed are placed in an STP disabled state.
An example will help you understand the concept:
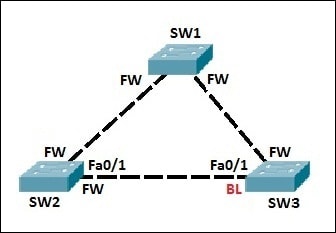
Let’s say that SW1 is elected as the root switch. All ports on SW1 are placed into forwarding state. SW2 and SW3 choose ports with the lowest cost to reach the root switch to be the root ports. These ports are also placed in forwarding state. On the shared Ethernet segment between SW2 and SW3, port Fa0/1 on SW2 has the lowest cost to reach the root switch. This port is placed in forwarding state. To prevent loops, port Fa0/1 on SW3 is placed in blocking state.
A switch with the lowest switch ID will become the root switch. A switch ID consists of two components: the switch’s priority (by default 32,768 on Cisco switches) and the switch’s MAC address.
BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit)
BPDUs are messages used by switches to share STP information with each other in order to elect a root switch and detect loops. The most common messages are Hello BPDUs which include the following information:
- root switch ID
- sender’s switch ID
- sender’s root cost
- Hello, MaxAge, and forward delay timers
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training: