ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is a network layer protocol that reports errors and provides information related to IP packet processing. ICMP is used by network devices to send error messages indicating, for example, that a requested service is not available or that a host isn’t reachable.
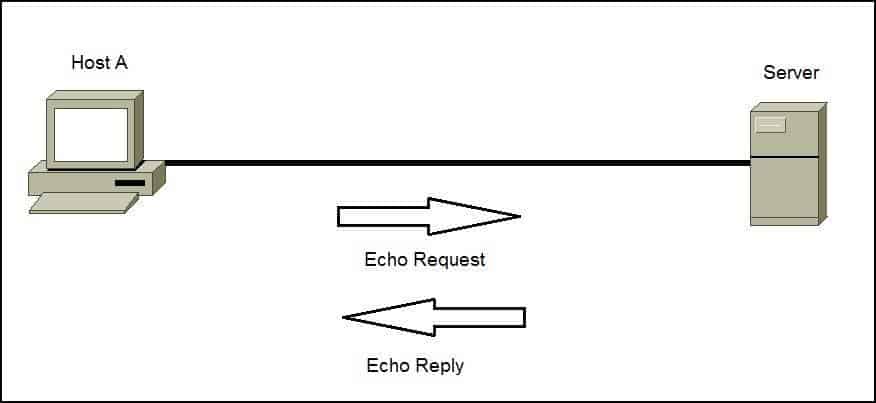
ICMP is commonly used by network tools such as ping or traceroute. Consider the following example that illustrates how ping can be used to test the reachability of a host:
Host A wants to test whether it can reach Server over the network. Host A will start the ping utility that will send ICMP Echo Request packets to Server. If Server is reachable, it will respond with ICMP Echo Reply packets. If Host A receives no response from Server, there might be a problem on the network.
ICMP messages are encapsulated in IP datagrams, which means that they don’t use higher level protocols (such as TCP or UDP) for transmission.
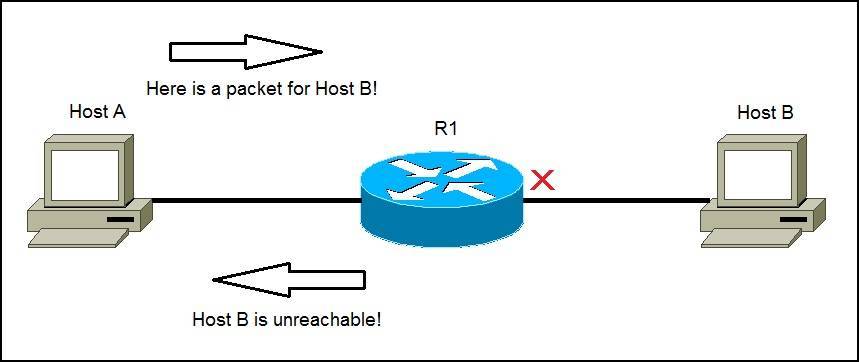
One other common ICMP message is the Destination unreachable message. Here is an example:
Host A sends a packet to Host B. Because the Host B is down, the router will send an ICMP Destination host unreachable message to Host A, informing it that the destination host is unreachable, e.g.:
C:\>ping 192.168.8.11
Pinging 192.168.8.11 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Ping statistics for 192.168.8.11:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss)
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training: