ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is a network protocol used to find out the hardware (MAC) address of a device from an IP address. It is used when a device wants to communicate with some other device on a local network (for example on an Ethernet network that requires physical addresses to be known before sending packets). The sending device uses ARP to translate IP addresses to MAC addresses. The device sends an ARP request message containing the IP address of the receiving device. All devices on a local network segment see the message, but only the device that has that IP address responds with the ARP reply message containing its MAC address. The sending device now has enough information to send the packet to the receiving device.
ARP request packets are sent to the broadcast addresses (FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF for the Ethernet broadcasts and 255.255.255.255 for the IP broadcast).
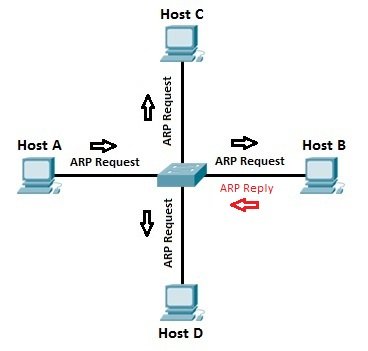
Here is the explanation otf the ARP process:
Let’s say that Host A wants to communicate with host B. Host A knows the IP address of host B, but it doesn’t know the host B’s MAC address. In order to find out the MAC address of host B, host A sends an ARP request, listing the host B’s IP address as the destination IP address and the MAC address of FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF (Ethernet broadcast). Switch will forward the frame out all interfaces (except the incoming interface). Each device on the segment will receive the packet, but because the destination IP address is host B’s IP address, only host B will reply with the ARP reply packet, listing its MAC address. Host A now has enough information to send the traffic to host B.
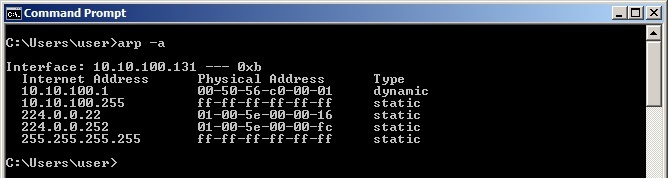
All operating systems maintain ARP caches that are checked before sending an ARP request message. Each time a host needs to send a packet to another host on the LAN, it first checks its ARP cache for the correct IP address and matching MAC address. The addresses will stay in the cache for a couple of minutes. You can display ARP entries in Windows by using the arp -a command:
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training: